
And troubled oil-exporting countries like Angola and Venezuela are even closer to Russia, with a broadly similar trajectory over the last three decades.įrom that perspective, there is nothing left to explain: Russia is quite similar to its closest peers and any purported “political will” to do this or that is mostly window dressing. If you visualise the same data compared to other petroleum-products exporting nations like Qatar and the UAE, you will see a very similar debt-to-GDP ratio in recent years. The fact that Russia has large natural resources that account for a big share of its exports (which you allude to incredulously in your question) is a simple, verifiable fact. But the Russian economy is neither of those things. Incidentally, high debt-to-GDP ratios are not limited to the west, Japan has a famously high debt, even compared to other mature advanced economies.

We could argue about the culture but its political and socio-economical structure and its history, both recent and less recent, are definitely completely different and the comparison implied in the graph simply does not make sense. Russia is not, by any means, “another Western country”. Blatant example: Shell losing control of the Sakhalin project after funding the whole startup, e.g. For the same reason as there's been much reluctance to invest, given that your company may get suddenly kicked out or management may be threatened with takeovers etc. There's also the factor that as a new and potentially unstable entity, there would have been a reluctance with many to lend Russia money. So basically, they have little debt because they've had little time to build it up. Thus they started from a relatively small debt, which Putin started paying in 2001 at the start of a resource boom and you're speaking of a country with a vast wealth of resources (diamonds, metals, oil). See this Congressional research report noting that servicing its debt in 1998 would have cost 80-90% of the anticipated Russian federal revenue. ), until the world (i.e., the "Club of Paris") forgave all but $60 Billion of debts in 1998. Then it teetered on the brink of chaos, lurching from crisis to crisis ( four debt restructurings before 1998, hyperinflation.
There Russia inherited both all its foreign properties (think embassies), and all its debt (but it still threatens to call in those non-Russian debts, occasionally see above reference). The USSR would lend to "Red" developing nations, and to Cuba of course similarly the GDR would lend to the USSR.Īs Germany reunited after the fall of the Berlin Wall (late 1989), they were the mayor 'Western' creditor to the USSR, which then broke up into some 15 countries.
A few non-aligned countries would lend to the USSR (e.g., Kuwait, which was repaid in 2016) but many of those were third-world countries (i.e., not in a position to lend). Given that the country could presumably have renegotiated its debtīurden, as most other developing countries eventually succeeded inįirst there was the cold war, so "The West" wouldn't lend money to The USSR/Eastern Block. The Romanian dictator’s actions are especially puzzling Heat, and factories were forced to cut back because of limitedįew other modern leaders would have agreed with Ceausescu’s Romanians were forced to live through cold winters with little or no His poor nation to foreign banks during the 1980s debt crisis. Repaying, in the span of a few years, the debt of $9 billion owed by
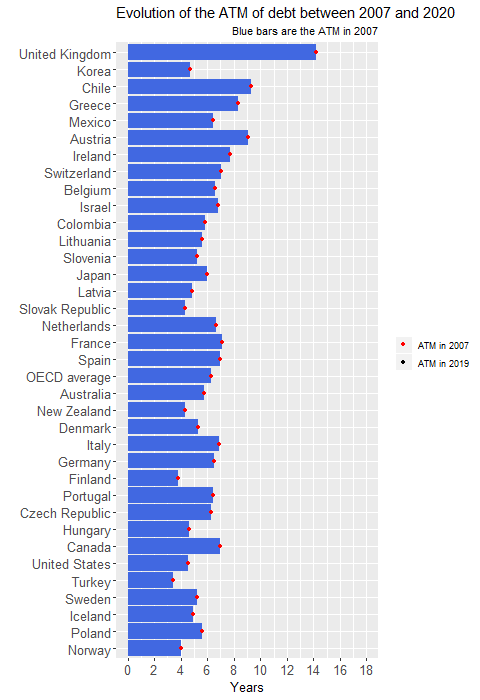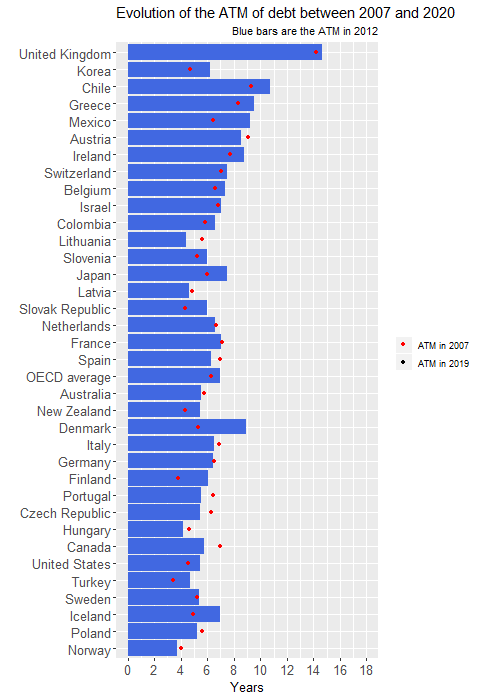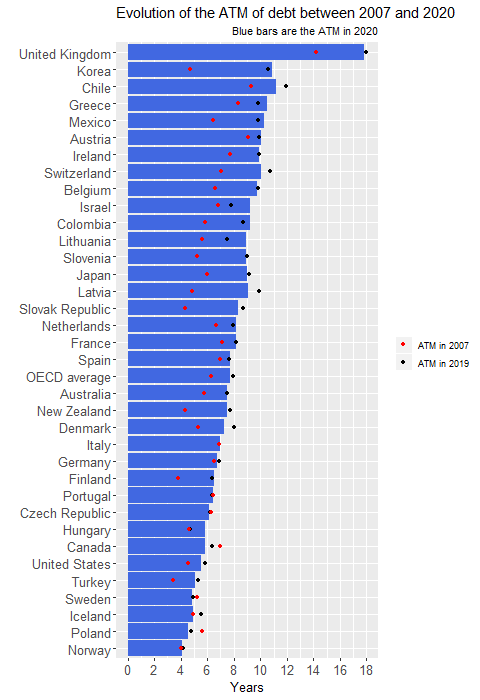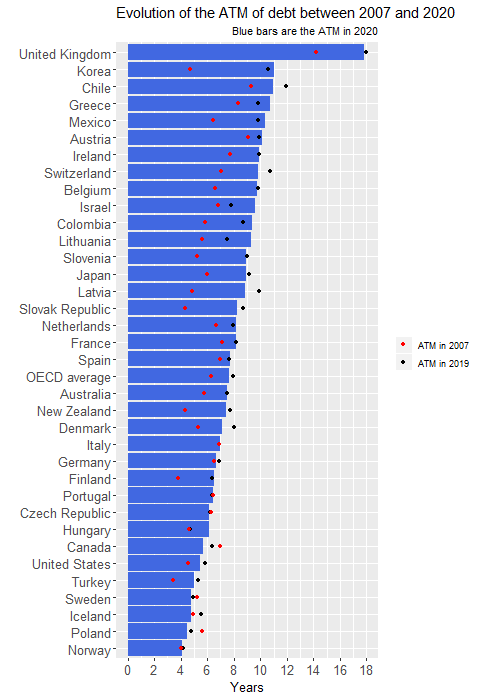
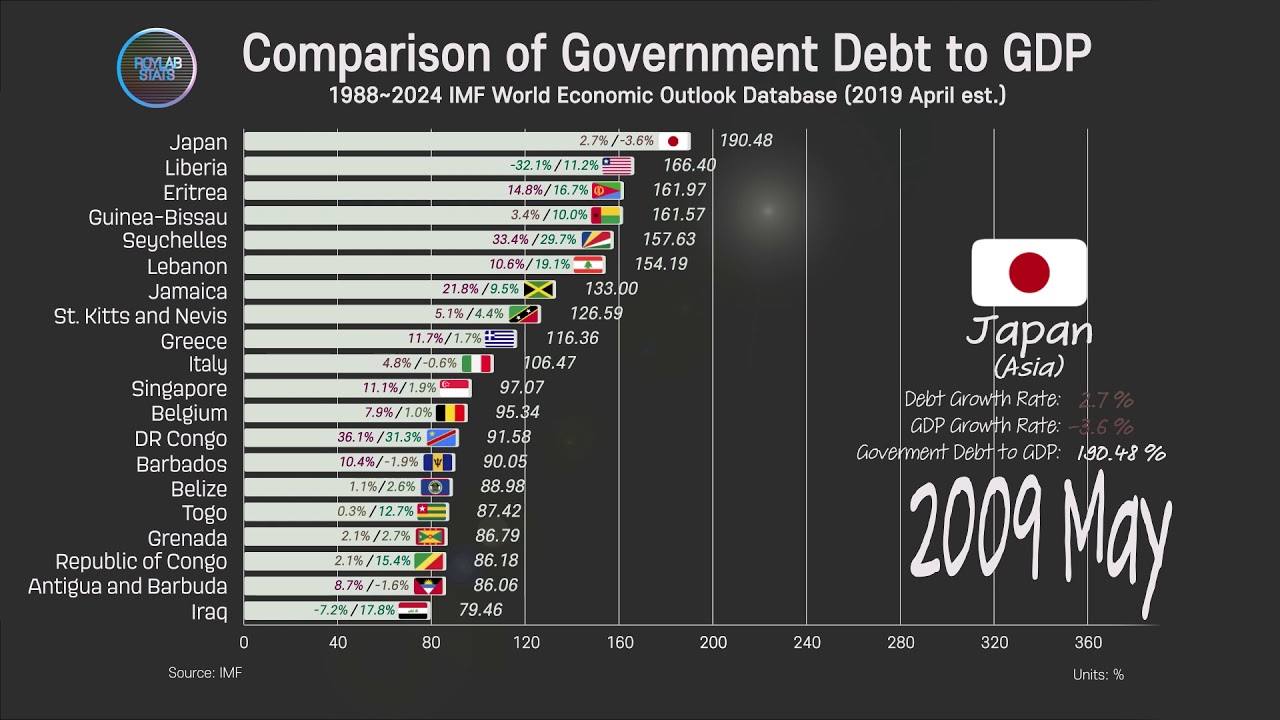
Romanian dictator Nikolai Ceausescu single-mindedly insisted on Side note: an example of political decision for debt reduction is given in this article Question: is Russia's debt size so small due to economic reasons only or are there any political reasons for this rather abrupt debt reduction? Quora answers indicate pure economical reasons (huge amount of natural resources and difficulty to borrow externally). This chart shows that Russia has a very low debt/GDP value compared to most of the other major countries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
